Exploring the Beauty of Processes: Differences and Applications of Lamination, Coating, and Bonding
2024.04.01Many people have similar confusion about the differences between "lamination," "coating," and "bonding" (composite). To put it simply, the combination of two different materials can be called "bonding" (composite). Based on this definition, lamination and coating are both methods of material composite. However, considering aspects such as the application field of the product, process technology, core key technologies, etc., the following, let us explore the differences between "lamination" and "coating."
Beyond Boundaries: Innovative Applications of Lamination and Coating Processes in Different Industries
Lamination application are typically in flexible packaging materials, such as food packaging materials that require the composite of one or multiple layers of plastic to enhance product durability and aesthetics, for instance, packaging for printing purposes often involves paper or film substrates, or interior automotive decorative.
On the other hand, coating are employed for protective functions or to enhance specific properties such as scratch resistance, durability, and moisture resistance. These are commonly seen in various industries including construction (fireproof boards, seismic boards), automotive (shielding protective films, synthetic leather, batteries), medical (medicated patches, dressings, test samples), and electronics (lithium batteries, LCD substrates, IC boards). Substrates for coating can range from boards, aluminum foil, glass, to plastic films.

Lamination is applied in textiles and food containers, coating is applied in energy, IC substrates, and medical industry.
In addition to the differences in application, the distinction between lamination and coating can also be made based on the production line design. Basically, a lamination line includes one or two extruders, lamination die, winding and unwinding unit.
On the other hand, coating lines can be further divided into sheet-to-sheet coater and roll-to-roll coating machine. Sheet-to-sheet coater involves pumping system, slot die, and coating platform, primarily used for coating flat substrates such as glass and sheet materials, applied in industries such as optics, energy, medical, and semiconductor.

Sheet-to-sheet coater, application is glass windows with viscosity of 150 cps, precision of 0.01 mm, coating range of 1800 x 2500 mm
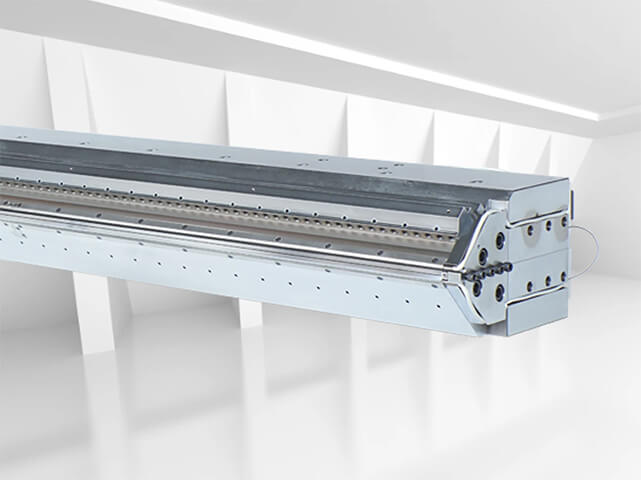
A roll-to-roll coating line includes pumping system, coating station (including slot die and comma rolls), winding and unwinding unit, and oven. It is primarily used for coating roll-shaped substrates like aluminum foil, copper foil, and films, with applications mainly in batteries or optics. These production lines are essential for efficiently applying coatings to continuous roll materials with precision and uniformity, meeting the specific requirements of industries focused on battery production or optical applications.
 S.jpg?vx4iuvw2a5)
A roll-to-roll production line for optical film coating, equipped with a slot die , coating range of 600mm
Compared with the multiple methods of coating such as blade, rolling coating, gravure, slot-die, and spraying, it's noted that the lamination is quite standardized. However, regardless of whether it's coating or lamination, dies play crucial role. This is because well-designed dies can meet product specifications by adjusting width, thickness, and other parameters. die also help reduce material wastage and maintain higher production efficiency.
Exploring Processes: The Key Role of dies in Lamination and Coating
As a core equipment in lamination production lines, lamination dies often operate under high-temperature conditions (average temperature around 350°C), primarily process plastic materials such as PP, PE, EVA, TPU, etc.
Depending on the lamination application, various designs are provided for both the die body and adjustment system.
For flexible packaging application, the four-piece structure of lamination die is predominant. The design of the lip angle allows it to closely adhere to the substrate, ensuring good coating effects within a short contact time with the material. Adjustment screws on both sides of the lip facilitate customer adjustments as per production line requirements, maintaining uniform output even at high speeds (line speed of 300 meters/minute).
For textile (woven/raffia) lamination, simple two-piece structure is common, with adjustment screws on one side of the lip and an internal deckle for width adjustment. This design is user-friendly for operators. Another design is tailored for high precision requirements and smart production. It features linear slide rails deckle system for width adjustment , and automatic bolts to reduce waste and losses.
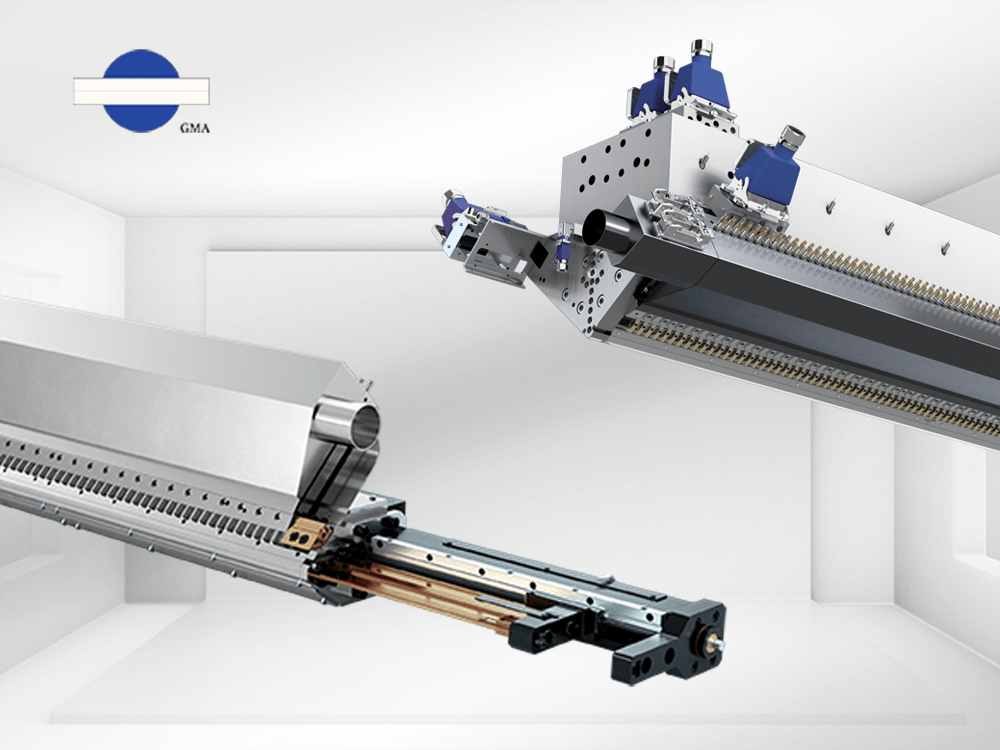
For multi-layers lamination, feed block with lamination die, or multi manifold structure lamination die can be utilized to achieve multi-layer layers
 From left to right: Four-piece structure dies
mainly used for flexibe packaging lamination, simple two-piece structure used
in woven or raffia lamination, and automatic lamination die for high precision
requirements.
From left to right: Four-piece structure dies
mainly used for flexibe packaging lamination, simple two-piece structure used
in woven or raffia lamination, and automatic lamination die for high precision
requirements.
Learn more: Complete Unlocking: Deckle system of extrusion die
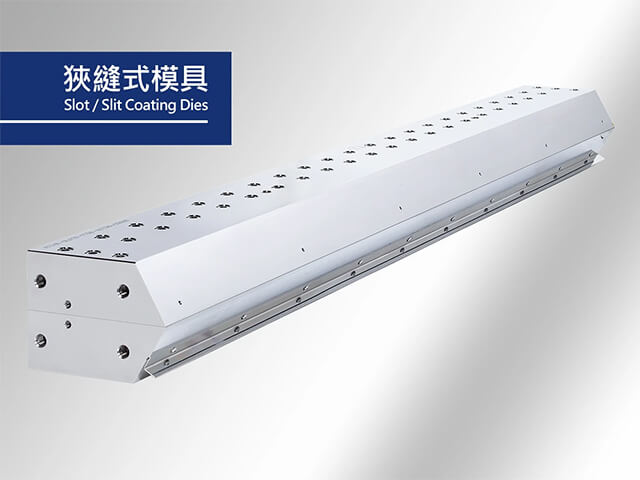
Coating dies, also known as "slot-die" due to the slit-like lip opening, are mostly operated at room temperature and are used to process various glue, such as epoxy resin, phenolic resin, acrylic resin, etc. Early coating techniques primarily revolved around roller-based technology. However, with the increasing demand for precision and environmentally friendly practices, slot dies have become widely adopted among various coating methods.
Slot die is enclosed operation, this is the major difference from traditional coating methods. Additionally, slot die offer several advantages:
- Reducing pollution caused by volatile compounds.
- Significantly lowering adhesive and post-use residue.
- Decreasing waste liquid output, thereby reducing production costs.
- Lowering downtime during operations, leading to reduced operating hours.
Moreover, slot die allows for continuous coating, effectively increasing coating speed. it also maintains precise coating thickness in both length and width directions.
Slot dies requires precise machining to avoid edge burrs or uneven surfaces during coating. After machining, the lip opening must maintain sharp edges with a diameter not exceeding 1 micron. The interior of the landing surface is processed using ultra-mirror finishing to effectively prevent material residue and ensure machining accuracy. This level of precision machining is critical for slot dies because unlike extrusion dies, slot die process various viscosities of glue at room temperature without the ability to adjust width using deckle system like extrusion die. Therefore, strict attention to detail is required in the design of the flow channels and machining accuracy.

Learn more: Rough? Not at all! The surface roughness is more detailed than you can imagine.
Slot dies are designed to meet various customer needs. For applications where multiple materials need to be mixed and coated, a standard slot die can fulfill the requirements. However, for cases where multiple materials need to be coated simultaneously without mixing, it is recommended to use slot die with multiple cavity layers. This design allows for separate channels for each material, ensuring precise and simultaneous coating without the need for mixing.

Low viscosity two-layers / Optical coating die / special lip process for battery
User relies on lab coating equipment for sampling and finding out the best formula of developing coating technology to save cost. This testing not only helps in reducing and managing production costs effectively during building production line setup but also serves as a reference for improving or upgrading existing coating equipment.
User acknowledges the importance of the test in early development but notes that it requires significant time and financial costs. They mention two main approaches in the market: setting up a dedicated laboratory and equipment, which is the most effective for long-term development but comes with higher costs, suitable for clients with coating experience looking to enhance their technology; and collaborating with professional laboratories to save costs, which is more suitable for clients in the early stages of coating development. Professional laboratories typically offer operational and technical support services and provide reliable reference data through their equipment.

Professional laboratories offer operational and technical support services, besides that also provide roll-to-roll pilot (left) and sheet-to-sheet pilot (right) for test
Learn more: Let us work together to create more possibility of coating techonology
User emphasizes the importance of high-end precision processes in both lamination and coating technologies, highlighting the need for keeping moving with bold innovation to meet the diverse and rapidly changing market demands. They also mention that upgrading essential core equipment and improving technological expertise are critical factors in strengthening competitiveness.