From Manual Adjustments to Automated Dies: Solving Precision and Waste
2024.12.30In extrusion production lines, the extrusion die stands as the key component. After the processes of melting and compounding in the earlier stages of the production line, plastic passes through the extrusion die to form the required product width and thickness. Once it exits the die, it undergoes shaping and stabilization. Given its pivotal role, the extrusion die is indispensable, especially grade films or coatings, medical supplies, and electronic components.
Beyond requiring high-precision machining, extrusion dies must ensure product quality with consistent and stable control. Over the years, the demand for automated dies has significantly increased, especially in recent years, as they offer enhanced capabilities for maintaining product quality.
What is an Automated Die?
An automated die, simply put, replaces the traditional extrusion die's manual adjustment mechanism for die lip openings with an automatic control system. This allows for finer thickness adjustments during production, resulting in benefits such as improved product quality (more uniform thickness), reduced raw material waste, and lower production costs.

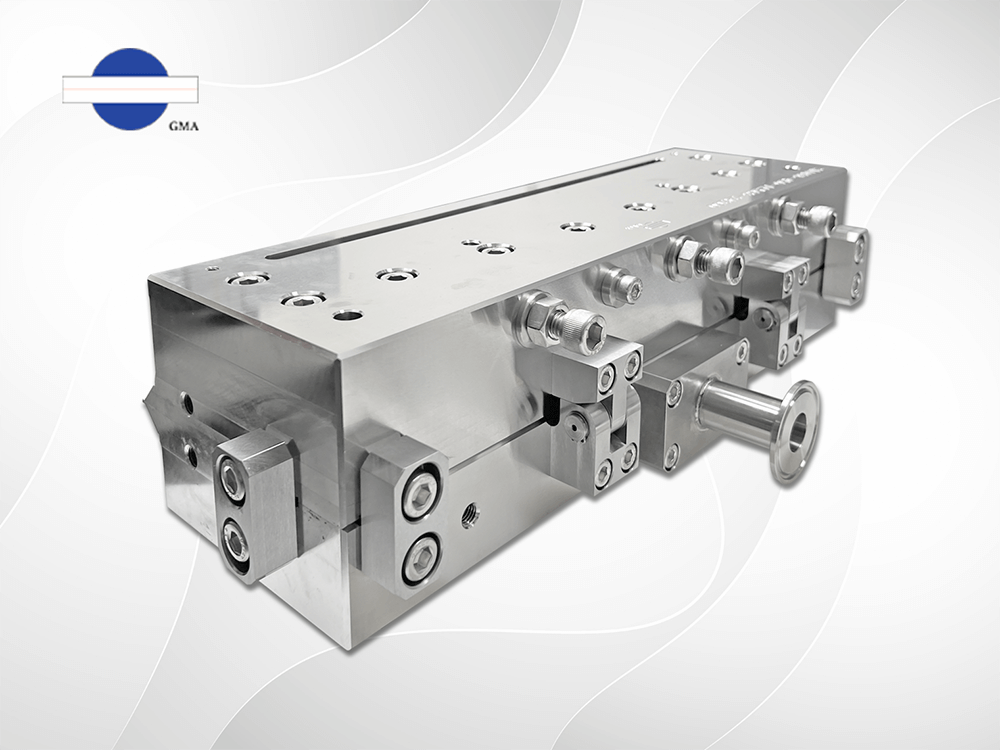
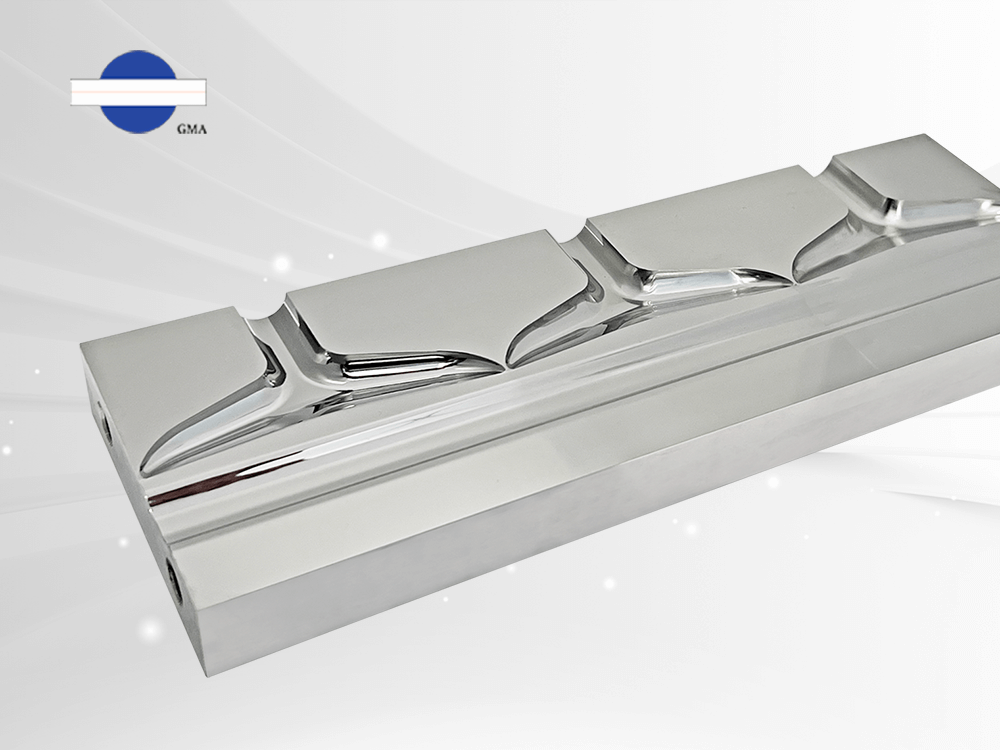
Automated die use an automatic bolts control system(right photo) to replace the traditional screw-adjusted die lip mechanism(left photo) in extrusion dies.
Differences Between Traditional and Automated Dies
Traditional extrusion dies commonly rely on manual bolt adjustments to control the die lip opening and thereby regulate product thickness. However, this method comes with several limitations:
1. Lack of Precision
The adjustment bolts for die lips depend on the gaps in the threads to determine the adjustment range. When the required adjustment range is smaller than the thread gap, achieving precision becomes difficult.
For example, with differential screws, where each turn adjusts 0.5mm, achieving an adjustment of 0.25mm becomes nearly impossible to control with accuracy.

Traditional extrusion dies via thread gaps determine the adjustment range.
Read more: Three Key Techniques for Adjusting Lip Opening in Extrusion Dies
2. Variability in Manual Operation
Since the bolts are adjusted manually, differences in technique among operators can lead to inconsistencies and errors. If adjustments are made outside of the production process, tools can be used to measure and correct the discrepancies. However, during production, it is not feasible to use tools to individually verify and correct adjustments. This makes it highly likely for variations to occur due to differences in operator methods and experience, resulting in greater inconsistencies.
3. Excessive Response Time
In practice, operators use tools or instruments to measure width and thickness to ensure quality control. If the thickness data is found to be non-compliant, adjustments are made to the die lip gap. After the adjustment, the next batch of products must be inspected to confirm whether the correction was successful. This back-and-forth process consumes a significant amount of raw material and time, leading to substantial production costs.
The second and third issues become even more pronounced when dealing with different production batch specifications, as more time and raw materials may be wasted during the adjustment process.
4. Difficulty in Online Adjustments
During production, the design of the production line structure may make it challenging for operators to adjust the screws.
Additionally, it is difficult to estimate the time required for adjustments.
In high-temperature production environments, these challenges pose significant safety risks to operators.
In contrast, automated dies, when paired with a feedback-based thickness gauge, operate by measuring real-time thickness data online. The automated bolts can instantly adjust the die lip openings based on production data, with each adjustment movement accurately controlled to 0.25mm. This ensures that product thickness remains within much tighter tolerance ranges.
The response time for adjustments and the time required to repeatedly verify whether the adjustments are complete are significantly faster than in traditional die production lines. This not only reduces raw material waste and production time but also eliminates the safety risks associated with manual online adjustments.

Automated dies (left photo) operate in conjunction with a feedback thickness gauge (right photo), allowing the automatic bolt adjustment stroke to be precisely controlled.
How Automated Dies Operate
The automatic control system consists of two components: hardware and software. The hardware refers to the mechanism installed on the extrusion die, which replaces the traditional bolt adjustment system. There are several design options available on the market, with the key differences being the method used to drive the adjustment bolts for die lip spacing. These include:
1. Pneumatic System
Uses air pressure to control and drive the bolts.
2. Heating System (Electric Heating Tubes)
Utilizes the physical principle of thermal expansion and contraction, where the electric heating tubes are controlled to maintain a consistent temperature, driving the bolts accordingly.
3. Mechanical System (Micro-Motors)
Employs micro-motors to drive the bolts, with precise control over their output.

Automatic adjustment bolts have different driving methods: pneumatic, electrothermal (heaters, left photo), and mechanical (micro motors, right photo).
Each driving method has its unique advantages and has been applied to extrusion and coating production lines. The choice of the appropriate automatic control bolts depends on the specific needs of the production line.
While software programs for automatic controllers vary among manufacturers, they generally share the following common features:
1. Compatibility with Thickness Gauges
The software can connect to thickness gauges from various brands and models, enabling the acquisition of real-time measurement data.
2. User-Friendly Interface
The interface is designed to be clear and simple, making it easy for operators to learn and use.
3. Data Integration and Export
The system allows internal data to be exported or integrated, facilitating production traceability and record-keeping.
 The user interface is simple
and intuitive, making it easy for operators to get started.
The user interface is simple
and intuitive, making it easy for operators to get started.
In recent years, the global labor shortage has prompted many manufacturers to consider using automated equipment to reduce production costs while maintaining or even improving product quality. However, upgrading from a traditional production line to an automated one requires a significant initial investment, which is a primary reason many remain hesitant to adopt this technology.
Another concern for manufacturers is finding a suitable supplier. Beyond providing high-quality hardware, suppliers must also offer robust technical support during the implementation of automated die systems. This is a common issue that customers worry about when transitioning to automation.
The AI Evolution of Extrusion Dies—Automated Dies
For M Company, a manufacturer specializing in optical films, these concerns are all too familiar. Like many other companies, M Company was significantly impacted during the pandemic. However, instead of a post-pandemic market recovery, they faced a chaotic landscape where numerous substandard products flooded the market at low prices, disrupting the competitive order.
As a company committed to quality, M Company decided to strengthen its market position by investing in production line upgrades. They replaced traditional dies with automated dies and thickness gauge systems. After these improvements, the production line quickly stabilized. Although the introduction of the new system initially caused some challenges for the existing production staff, the system’s ease of use, combined with training and a brief adjustment period, enabled operators to adapt swiftly. This not only reduced their workload significantly but also helped bridge previous production gaps effectively.

Although the initial investment cost of an automated die system is relatively high, its ease of operation and high precision provide users with significant long-term benefits.
As discussions around AI (Artificial Intelligence) increasingly focus on its potential to replace certain human jobs, automated dies can be seen as the "AI" of the extrusion die industry. By integrating hardware and software systems, automated dies address critical control issues in extrusion production lines. While they cannot completely replace human operators, they effectively assist them in boosting productivity and reducing unnecessary production costs. If AI represents the inevitable trend of the future, then automated dies are undoubtedly the best tool for businesses looking to capture greater market opportunities.