The Multiverse of Extrusion Dies: Flat, Profile, and Multi-Layer Coextrusion Dies
2025.01.23The Versatility of Extrusion Processes
Extrusion, an essential process in modern industries, is widely applied to the forming of various materials. Examples include aluminum extrusion (metal extrusion) for products such as aluminum window frames and automotive part casings; food extrusion for items like pasta and candies; ceramic extrusion for manufacturing ceramic filter cores used in filtration systems; rubber extrusion for products like seals and rubber tubes; and plastic extrusion for items like sheets (films) and plastic pipes.
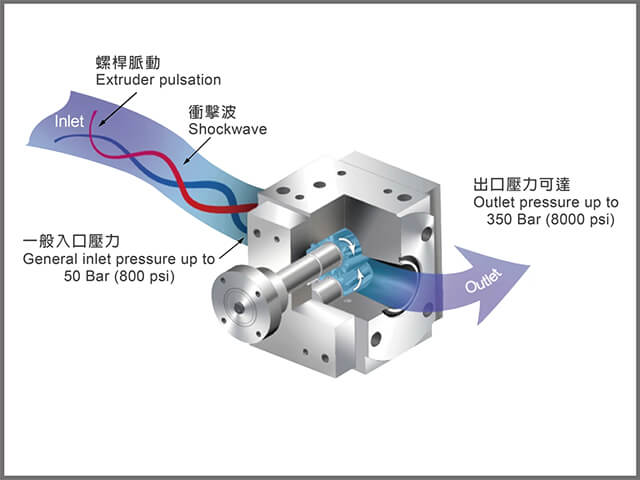
Extrusion processes are heavily utilized in plastic molding and, along with injection molding, represent the two primary methods of plastic forming. In extrusion, plastic pellets are heated and softened through an extruder mechanism, transforming them into a pliable liquid state. This material is then subjected to high pressure and forced into a mold or die, creating objects with specific cross-sectional shapes. This process offers high production efficiency and remarkable flexibility. The critical component in extrusion molding is the "extrusion die."
Read more: Here are 10 key points to understand extrusion dies
What is an "Extrusion Die"? What are its Types?
Based on the shape and application of the mold, extrusion dies can be categorized into the following types:
1. Aluminum Extrusion Die
Aluminum alloy is currently one of the most widely used metals in the industry. Therefore, this type of die is specifically designed for manufacturing aluminum and alloy parts.
Applications include the aerospace, automotive, marine, construction, motor housing, and mechanical framework industries.

Aluminum extrusion dies are primarily used to produce aluminum alloy components, widely applied in construction and structural frameworks.
Die casting dies are similar to aluminum extrusion dies but are used for forming a wider range of metal materials, such as zinc, magnesium, and copper alloys. These dies are commonly applied in the production of gears, automotive interior components, valves, and other mechanical parts.
 The difference between die casting dies and aluminum extrusion dies lies in their application scope. Die casting dies handle a wider variety of metal materials and are used to produce many types of mechanical components.
The difference between die casting dies and aluminum extrusion dies lies in their application scope. Die casting dies handle a wider variety of metal materials and are used to produce many types of mechanical components.
2. Profile Extrusion Dies
Profile extrusion dies are mostly used for producing various types and sizes of pipes, such as plastic pipes and hoses. They are also used to manufacture construction materials like plastic door frames, wood-plastic flooring, and roofing materials.
A similar type of die is the hollow profile extrusion die, which may refer to aluminum extrusion dies designed for producing hollow aluminum alloy products. It can also refer to profile extrusion for creating plastic window frames, wood-plastic flooring, or hollow plastic sheets (also known as corrugated sheets). For easier distinction, the latter is often referred to as "hollow flat sheets."
 (Left) Profile Extrusion Dies are specifically designed for producing pipes. (Center) Hollow Profile Extrusion Dies are used for manufacturing metal or plastic frames.(Right) Another type of hollow die, also known as a hollow flat sheet extrusion die, is used for producing hollow plastic sheets.
(Left) Profile Extrusion Dies are specifically designed for producing pipes. (Center) Hollow Profile Extrusion Dies are used for manufacturing metal or plastic frames.(Right) Another type of hollow die, also known as a hollow flat sheet extrusion die, is used for producing hollow plastic sheets.
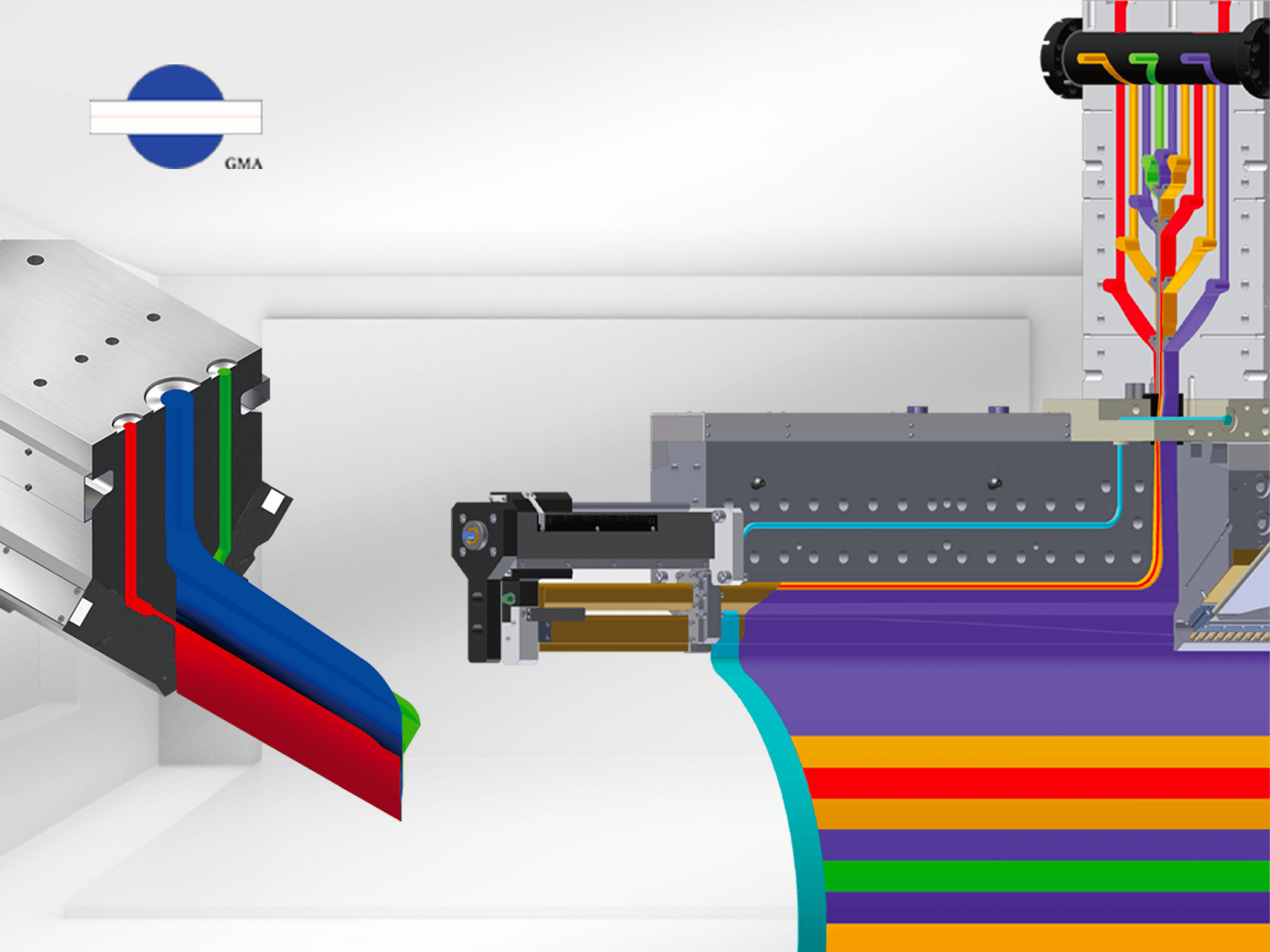
3. Multi-Layer Coextrusion Dies
Products made from multi-layered plastics can be produced through different processes, using two types of multi-layer film dies: blown film dies and flat multi-layer dies (also called multi manifold die). The differences between these two are as follows:
|
|
Blown film dies |
Flat multi manifold die |
|
Film production method |
The material is inflated vertically using a circular die to form a tubular shape, which is then cut into flat films. |
he material is evenly stretched horizontally into film using a flat die. |
|
Cooling way |
Air cooling |
Roller cooling |
|
layers |
Typically produces 3–9 layers, but the thickness between layers is more difficult to control. |
Can produce over 100 layers, with precise control over the thickness of each layer. |
|
Die structure |
Round mold |
Flat die with single chamber or multiple chambers |
|
Film Characteristics |
Thickness uniformity is harder to control, but the film offers better puncture resistance and impact strength, making it suitable for general applications. |
The thickness between layers can be precisely controlled, resulting in a smoother film surface with excellent optical transparency and tear resistance. |
|
Application |
Primarily used for flexible packaging, including frozen food bags, vacuum packaging, agricultural films, shrink films, and garbage bags. |
Primarily used for high-precision applications, such as optical protective films, touch screens, multi-layer barrier films for food, lithium battery separators, and photovoltaic backsheet films. |
|
Advantage |
Features fast production speed, easy operation, and low equipment costs. |
Allows precise control for stable product quality and is suitable for a wider range of applications. |
 (Left) Blown Film Die: Primarily used for producing various flexible packaging materials, such as plastic bags. (Right) Flat Multi-Layer Die: Used for producing high-precision optical films.
(Left) Blown Film Die: Primarily used for producing various flexible packaging materials, such as plastic bags. (Right) Flat Multi-Layer Die: Used for producing high-precision optical films.
Read more: Innovation in Co-Extrusion Process: Multi Manifold Die
4. Flat Extrusion Die
Flat extrusion dies are composed of two or more flat steel plates joined together. Due to the internal flow channel design often resembling a T-shape, they are sometimes referred to as T-dies. However, in practice, as plastic materials evolve rapidly, the flow channel design has expanded beyond the single T-shape to include structures such as coat-hanger shapes, fishtail designs, and multiple cavity designs to ensure uniform plastic flow within the die cavity.
The die structure can also be tailored to practical requirements and may incorporate automated control systems, width adjustment systems, and thickness adjustment systems. These dies are widely used in production lines for sheets, films, lamination, hollow sheet, foaming materials, and filament extrusion.
 Flat extrusion dies, to meet diverse applications, can be equipped with systems such as automatic control, width adjustment, and thickness adjustment.
Flat extrusion dies, to meet diverse applications, can be equipped with systems such as automatic control, width adjustment, and thickness adjustment.
Read more : Mold Flow Analysis: Unlocking Precision in Extrusion Die Design
Flat extrusion dies, due to varying application fields, have evolved into meltblown and spunbond dies. The former is used for producing meltblown fabric (also known as nonwoven fabric), commonly applied in mask filter layers and filter cores. Additionally, coating dies—another derivative—are utilized in critical coating processes for new energy industries (such as solar energy, energy storage batteries, and lithium batteries), semiconductors, and medical products. These dies are characterized by extremely small slit openings and are often referred to as slot dies.
 Extrusion dies, due to varying application fields, have evolved into coating dies (left, also known as slot dies) and meltblown dies (right).
Extrusion dies, due to varying application fields, have evolved into coating dies (left, also known as slot dies) and meltblown dies (right).
Read more : Let us work together to create more possibility of coating technology
Extrusion dies are the core of the plastic extrusion process, with flat extrusion dies being particularly critical. To meet diverse applications and high-precision requirements, the design and manufacturing of flat extrusion dies demand meticulous attention to detail and exceptional precision. The technical barriers to entry are high, which makes it a less common field of expertise. However, flat extrusion dies remain one of the essential cornerstones of modern industrial manufacturing. Despite the challenges and obstacles, this field is also filled with limitless possibilities and opportunities for innovation.